The Normal Pulse Rate Explained: Age-Based Ranges and Factors That Affect It
Meta Description:
What is the normal pulse rate? Discover age-based ranges, factors affecting heart rate, and tips to maintain a healthy pulse. Contact us for personalized advice!
Introduction
Your heart is the engine that keeps your body running, and your pulse rate is a key indicator of its health. But what is the normal pulse rate, and how does it vary with age? Whether you’re an athlete monitoring your fitness or someone simply curious about your health, understanding your pulse rate is essential.
In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore:
- What a normal pulse rate is and why it matters.
- Age-based pulse rate ranges for children, adults, and seniors.
- Factors that can affect your heart rate, from exercise to stress.
- Tips to maintain a healthy pulse rate and when to seek medical advice.
By the end of this article, you’ll have a clear understanding of your heart’s rhythm and how to keep it in check. Let’s dive in!
What Is the Normal Pulse Rate?
Your pulse rate, also known as your heart rate, is the number of times your heart beats per minute (bpm). It’s a vital sign that reflects your cardiovascular health. But what is the normal pulse rate for an average adult?
According to the American Heart Association (AHA), a normal resting heart rate for adults ranges from 60 to 100 bpm. However, factors like age, fitness level, and overall health can influence this range.
Key Points:
- Resting Heart Rate: The heart rate when you’re at rest, typically measured in the morning before any physical activity.
- Target Heart Rate: The ideal range during exercise, usually 50-85% of your maximum heart rate.
- Maximum Heart Rate: The highest heart rate your body can handle during intense activity, calculated as 220 minus your age.
For example, a 30-year-old’s maximum heart rate would be 190 bpm (220 – 30 = 190).
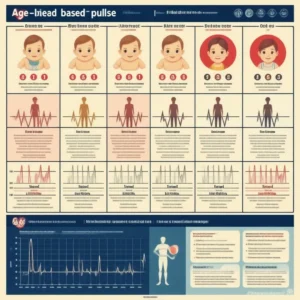
Age-Based Pulse Rate Ranges
Your pulse rate changes as you age. Here’s a breakdown of normal pulse rates by age group:
1. Infants and Children
- Newborns (0-1 month): 70-190 bpm
- Infants (1-11 months): 80-160 bpm
- Toddlers (1-2 years): 80-130 bpm
- Preschoolers (3-5 years): 80-120 bpm
- School-Age Children (6-15 years): 70-100 bpm
Children typically have higher heart rates than adults due to their smaller hearts and faster metabolism.
2. Adults (18-64 Years)
- Normal Resting Heart Rate: 60-100 bpm
- Athletes or Highly Active Individuals: 40-60 bpm
Athletes often have lower resting heart rates because their hearts are more efficient at pumping blood.
3. Seniors (65+ Years)
- Normal Resting Heart Rate: 60-100 bpm
- Slightly Higher Rates: Due to age-related changes in cardiovascular health, seniors may have slightly higher resting heart rates.
Factors That Affect Your Pulse Rate
Several factors can influence your heart rate, including:
1. Physical Activity
Exercise temporarily increases your heart rate. Regular physical activity can lower your resting heart rate over time.
2. Stress and Emotions
Stress, anxiety, and excitement can cause a spike in your heart rate.
3. Medications
Certain medications, like beta-blockers, can lower your heart rate, while others, like decongestants, can raise it.
4. Health Conditions
Conditions like anemia, thyroid disorders, and heart disease can affect your pulse rate.
5. Temperature and Hydration
Hot weather and dehydration can increase your heart rate, while cold temperatures may lower it.
How to Measure Your Pulse Rate
Measuring your pulse rate is simple and can be done at home. Here’s how:
- Locate Your Pulse: Place your index and middle fingers on your wrist (radial artery) or neck (carotid artery).
- Count the Beats: Count the number of beats in 60 seconds.
- Use a Pulse Oximeter: For a more accurate reading, consider using a pulse oximeter.
For more information on pulse oximeters, check out our guide on what is the normal range for an oximeter.
Tips to Maintain a Healthy Pulse Rate
Maintaining a healthy pulse rate is crucial for overall well-being. Here are some actionable tips:
1. Exercise Regularly
Engage in aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling to strengthen your heart.
2. Eat a Balanced Diet
Include heart-healthy foods like fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins.
3. Stay Hydrated
Dehydration can strain your heart, so drink plenty of water throughout the day.
4. Manage Stress
Practice relaxation techniques like deep breathing, meditation, or yoga.
5. Monitor Your Heart Rate
Use tools like pulse oximeters or fitness trackers to keep track of your heart rate.
For more tips on maintaining cardiovascular health, visit our anti-aging category.
When to Seek Medical Advice
While a normal pulse rate is a good sign, certain symptoms may indicate an underlying issue. Consult a healthcare professional if you experience:
- A resting heart rate consistently above 100 bpm (tachycardia).
- A resting heart rate below 60 bpm (bradycardia), especially if accompanied by dizziness or fatigue.
- Irregular heartbeats (arrhythmias).
For personalized advice, feel free to contact us or reach out via WhatsApp.
Conclusion
Understanding what is the normal pulse rate is essential for monitoring your heart health. By knowing the age-based ranges and factors that affect your heart rate, you can take proactive steps to maintain a healthy pulse.
Remember, your heart is your body’s most vital organ—take care of it! If you have any concerns about your pulse rate or overall health, don’t hesitate to contact us for expert guidance.